Data Update Cycles
May 22, 2025
Data is updated through a continuous gathering process. For most collections, data is collected in cycles — when one full scan completes, the next begins immediately.
Data gathering for each collection is performed independently and in parallel.
| Icon | Collection | Update Type | Average Cycle Duration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Responses | Cycle‑based | ~21 days | |
| DNS Registry | Cycle‑based | ~15 days | |
| IP WHOIS | Cycle‑based | ~30 days | |
| Domain WHOIS | Cycle‑based (with historical merge) |
~60 days | |
| Certificates | Continuous collection | – |
For the Domain WHOIS collection, we use a mixed update technique: each new index is collected from scratch, but once completed, we supplement it with data from the previous index. This approach helps preserve information about deleted, expired, or temporarily unavailable domains.
Certificates are continuously extended as new data becomes available.
All the data is collected independently by Netlas itself
We do not rely on third parties1 or aggregators — every record is obtained and indexed directly by the platform.
Indices
Data collected during each cycle is stored in a separate index.
The full list of currently available indices can be found on the About Page. As usual, we store several of the most relevant indices along with a number of historical indices covering the past few years.
When using Netlas Search Tools, you can specify which index to search by clicking the Index Selection button on the right side of the search bar.

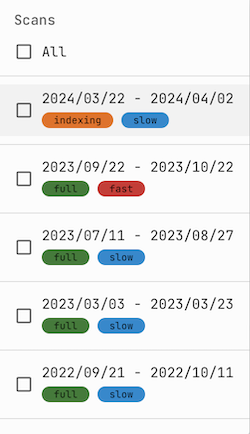
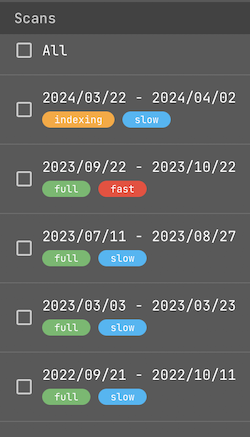
Changing the index can significantly affect search execution time. Pay attention to the labels:
fast – The index is stored in high-speed memory for quick access.
slow – The index is moved to slower-access memory, resulting in longer search times.
You may also have access to indices that are currently being updated:
indexing – The index is still being built; data collection is in progress.
full – The index has been fully built and is ready for searching.
Private Indices
Private indices are created when you use the Private Scanner. You can use them in the same way as regular (public) indices. The only difference is that private indices are available only to their creator and their teammates.
Private indices are not searched by default. You must explicitly select a private index to run queries against it.
Private indices are linked to scans in the Private Scanner. When you delete a scan, the associated private index is also deleted.
Accessing Most Recent Data
When using Netlas Search Tools, the best option is to search without specifying a particular index. This allows you to access the most recently collected complete portion of data.
The default request routing works slightly differently across the various search tools.
Internet Scan Data
For internet scan data, we divide the entire IPv4 address space into large subnets2. When a subnet is fully scanned, it automatically "replaces" the previous version in the default output, ensuring the latest complete coverage is always prioritized.
DNS and WHOIS Data
For DNS and WHOIS data, the most current and fully completed index is automatically selected as the default for searches.
-
The only exceptions are the threat intelligence data shown in the IP/Domain Info tool and the geolocation data, which are provided by Netlas partners. ↩
-
Currently using
/4networks. ↩